Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is a state wherein a canine is fixated on something in its current environmental factors, a spot on its body, or even by nonexistent things. The conduct does not serve any crucial part in the survival of the animal but somehow impacts its mental response and the way onlookers perceive the behaviour.

It has been discussed whether the term OCD is reasonable for canines. In canines, this conduct suddenly shows itself, it is also related to the kind of breed it is. At the point when the conduct persists and gets intense, there is a cause for concern, and a therapeutic intervention is required. What needs attention is that the behaviour should be observed and examined while it is at the nascent stage. Instead of perceiving the actions as adorable or amusing, and ignoring it for a considerable time, it calls for a behaviour change strategy.
Here are six stages you can take to manage a canine that is associated with having a behavioural concern:
Perceive the Signs
As expressed earlier, CCD is visible by an example of conduct that continues or repeats. In people, OCD is identified through such perceptible activities as obsessively washing one’s hands, locking and unlocking doors, or arranging everything in symmetrical order.
Recognize the Cause
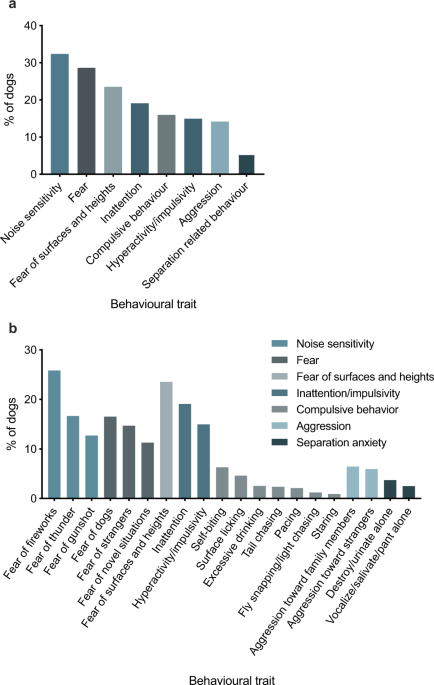
CCD behaniours are the means through which a canine attempts to comfort itself. Further, such practices can be set off due to struggle, confinement, genuine mishaps, unusual occurrences, or abrupt changes in a typical schedule the pet is used to.
Sometimes, a few practices, for example, a canine squeezing its head against a level surface, walking around, or going round and round, might not have anything to do with CCD. Advance research reveals an association between Canine Compulsive Disorder and Canine Chromosome 7. For instance, a canine that does not get a required amount of supplements may contract Pica, which is a condition where a canine impulsively devours non-food things. In like manner, extreme licking can result from an absence of Vitamin E and other supplements.

Comprehend the Effects
Unreasonable sucking and licking could hurt the skin and lead to bacterial diseases. The affected portion of the skin gets sore and a short while later may crack to shape into an injury or sore. In the process, the canine starts to give in to the tendency, probably even enjoy it. The result could be ‘lick granuloma’, or ‘lick dermatitis’.
Even though contaminations can be treated through anti-toxins, it is always the best to recognize and handle the underlying driver of the issue. The problem could simply lie in the insufficient nutritional requirements of the dog.
The canine OCD is similar to that found in people, engaging in sucking, licking, etc. The repeat behaviour lowers the intensity, and eases the discomfort and stress.

Try not to Enable Responses
As mentioned before, when the pet is a little dog, pursuing the tail can be seen as rather engaging and ends up being supported by the human friends. Overall, there is nothing noticeably destructive or so it appears.
As far as possible, refrain from getting angry, raising voice, or rebuffing the canine for its activities. Since nervousness can be a contributory factor, demanding discipline at that time, can add to pressure, prompting a boost in further undesirable actions.
It is the time to consult your vet. The involvement of a specialist prevents misdiagnosis. Dreary licking, for instance, can be brought about by parasites or even hypersensitivity. Different propensities can likewise be set off by cerebrum tumors or Cushing’s sickness.
Make a Healing Move

Problem behaviors such as excessive tail chasing, chewing, or digging could intensify as means of releasing pent-up energy. In addition, giving stuffed toys and other playthings can help distracting the canine while providing a stimulus to ease out and redirect its behaviour. It may include presenting a specific sound like a jingle to intrude on the enthusiastic conduct and take the canine back to the real world. On the occasions when the canine conduct is a consequence of stress or separation anxiety, it is ideal to use soothing sound tunes or recordings with relaxing pictures and videos.
The key is to keep the pet involved in activities that lift it out of a self-involved mindset, and stretch and stimulate its mind beyond innate insecurities.
Ultimately, try your best not to encourage the OCD conduct. Sometimes, a canine will simply engage in these self-hurtful exercises to acquire the owner’s attention, particularly if the latter’s responses are encouraging as opposed to remedial. At whatever point such is the situation, it is ideal to ignore the canine as it carries on with its activities.